
My colleague of near half a century, Peter Ryan, has produced a new edition of his popular 2017 photographic book, Guide to Seabirds of Southern Africa. With 40 more pages, the book is noticeably thicker than the first edition, but the same format will allow the two editions to sit nicely side by side in the seabird section of my study library. The publisher’s blurb has this to say:
“This revised, updated and expanded edition of Guide to Seabirds of Southern Africa remains the only book to focus exclusively on the seabirds of southern Africa and includes nine new species for the region. An expanded introduction covering seabird origins, moult, feeding, breeding, conservation, and how best to watch and photograph these iconic birds [and] a bonus feature on flying fish and flying squid”. Worthy of a new review then, following on from my original in ACAP Latest News in April 2017.
Ryan#2 covers 142 seabird species which have been recorded (by specimens, accepted sightings, photographs or by tracking) in southern African waters and in the Southern Ocean and its oceanic islands south of Africa. It is always tricky to decide what birds associated with the marine environment to include. Peter takes what is perhaps a conservative view: there are no pelicans or grebes included, despite there being records of species of both groups, notably of the Great White Pelican Pelecanus onocrotalus and Black-necked Grebe Podiceps nigricollis, occuring pretty regularly close inshore in South African and Namibian waters, mainly in sheltered bays. This contrasts with Peter Harrison's seabirds of the world book where both groups are included. I reviewed the second editIon of Harrison's book in an ACAP Monthly Missive earlier this year. However, Peter Ryan does include some "marginal' seabirds among the cormorants, gulls and terns. At least, unlike Harrison, who gives it a truncated account, he leaves out the Lesser Sheathbill Chionis minor of the Prince Edward Islands, a bird I know reasonably well, and one that at best is a shorebird that sometimes fossicks along the waters' edge. Really, there is no completely logical way in making the divide between sea and land!
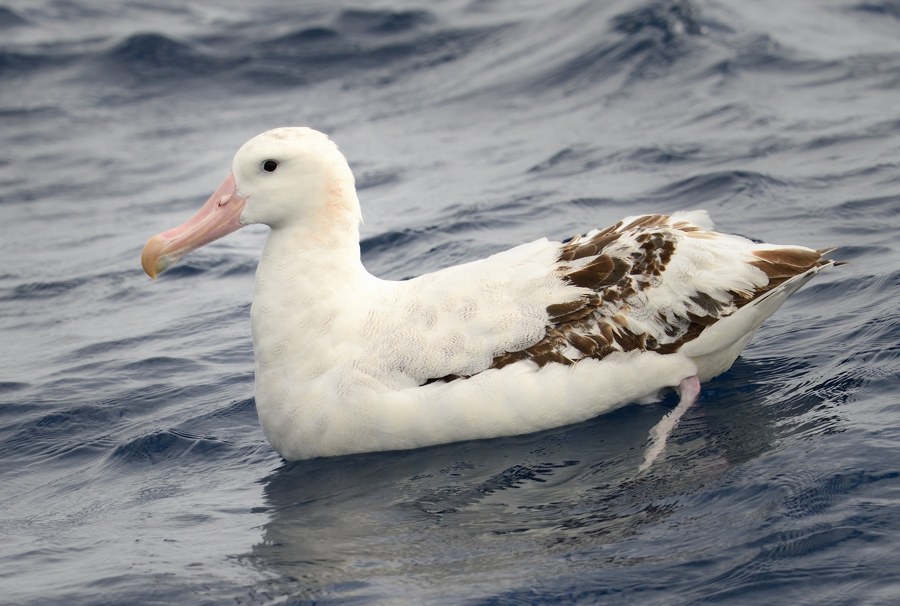

The next albatross for southern Africa? An adult Antipodean Albatross off North Cape, New Zealand, photograph by Kirk Zufelt
The nine new species since Ryan#1 (I had to carefully compare the two editions to find them) include the ACAP-listed Campbell Albatross Thalassarche impavida, a New Zealand endemic, known so far from only a single tracked adult south of Africa that was undergoing a circumnavigation of the Southern Ocean. Among the procellariiforms, the Mascarene Pseudobulweria atterima and the Tahiti P. rostrata Petrels are also new listings. Looking at coverage, there are many new photos adding to the book’s length. For example, the section on the six species of prions Pachyptila spp. has increased from four to seven pages, affording each species a full page with more photos in the second edition.
There have been some name changes as well, reflecting new taxonomic thinking. The rockhopper penguins of the Prince Edward Islands are now considered to be the Eastern species Eudyptes filholi, and no longer a subspecies of the Southern E. chrysocome. In contrast, and unlike ACAP’s and BirdLife International’s treatments, the White-capped Albatross T. steadi remains as a subspecies of the Shy Albatross T. cauta across both editions. No less than 18 of the 22 species of albatrosses recognized by ACAP have been recorded in waters covered by the guide, some only as very rare vagrants. Three of the four Phoebastria albatrosses of the Pacific and the New Zealand endemic Antipodean Albatross Diomedea antipodensis are missing. I was lucky enough to be shown at sea the first ever and perhaps the only Laysan Albatross P. immutabilis to be spotted in the southern African region by Peter Harrison on our way to Marion Island way back on 29 April 1983 (click here). The Antipodean seems the most likely to turn up, but it is notoriously difficult to separate with any certainty from several of the other great albatrosses when sighted at sea, especially from the Tristan Albatross D. dabbenena. So it may have to be a tracked bird to make Ryan#3! Two of the five ACAP-listed Procellaria petrels, both endemic to New Zealand, have not yet been recorded in southern African waters. They are the Black. P. parkinsoni and the Westland P. westlandica. The only other ACAP-listed species not yet recorded for southern Africa is the Pink-footed Shearwater Ardenna creatopus of the South Pacific. Remarkably then, 24 of the 31 ACAP-listed species are featured in Peter Ryan’s guide.
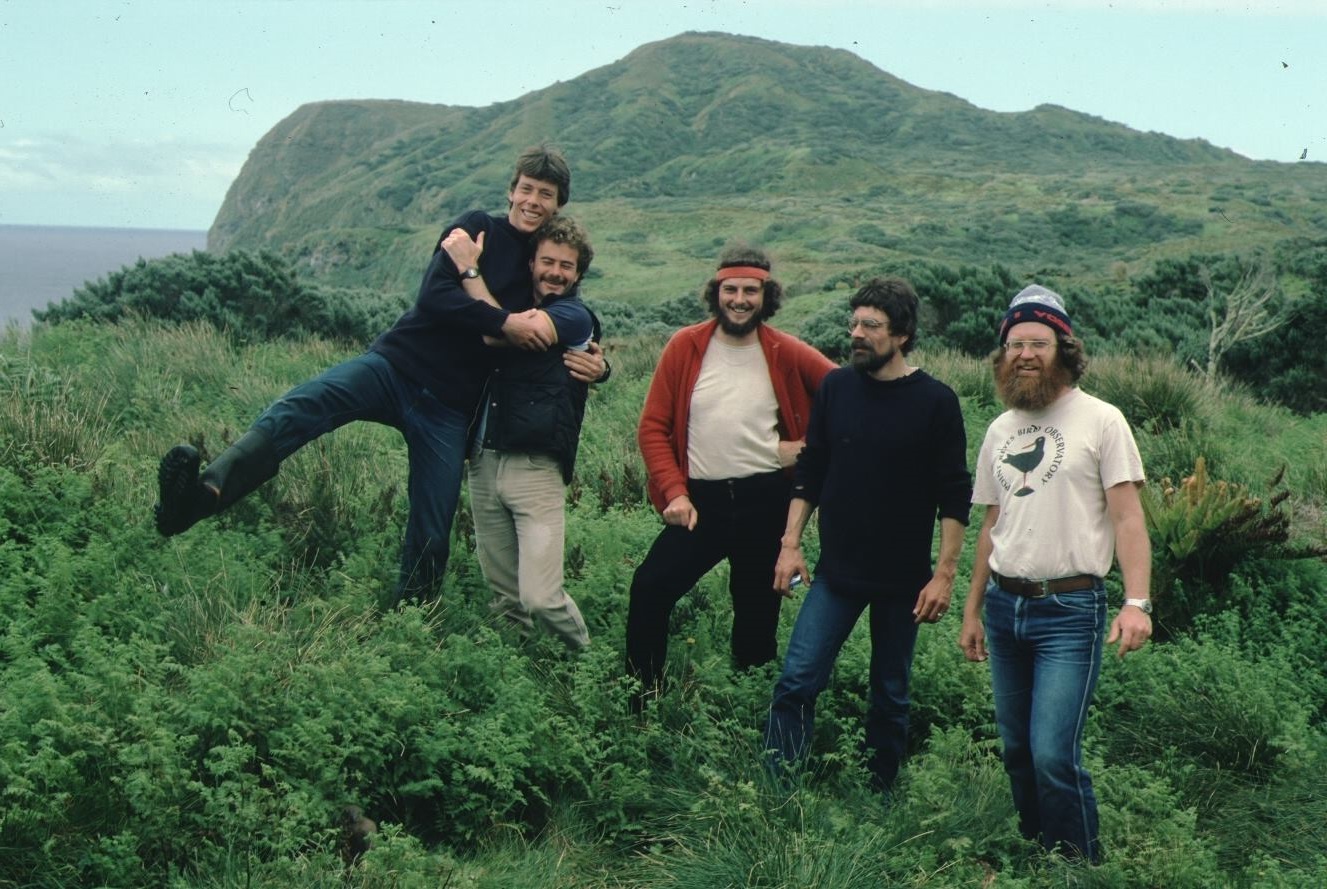 It's way back in 1984 and the ‘Fitztitute’ team is hamming it up for the camera on Gough Island. Peter is on the left, I am on the right, with Barry Watkins, Stevi Broni and the late Jim Enticott
It's way back in 1984 and the ‘Fitztitute’ team is hamming it up for the camera on Gough Island. Peter is on the left, I am on the right, with Barry Watkins, Stevi Broni and the late Jim Enticott
Intriguingly, the new edition includes some non-avian flying animals. The ommastrephid flying squid Peter has photographed have yet to be identified to species; likewise he has photographed many varieties of flying fish, all of the family Exoceotidae, also without being able to assign them to species. Some of them are remarkably colourful and handsome. I learnt a deal more than I already knew about these little-studied animals from the five pages of text and photos. No bats seen flying over the sea as yet!
The font used throughout both editions is a rather a small one. I had no problem with this back in 2017, but this year I have dumped my long-worn multifocals after cataract operations and am now struggling to read the text without resorting to a magnifying glass under a bright light! I have resisted getting reading glasses since the operation on medical advice but may now have to give in. On the plus side, the small font and small maps and equally small but well-chosen photos keep the book a suitable size for field work. In fact, it should fit into one of those cargo pockets on the hiking vests some birders like to wear.
Ryan#2 keeps the book’s dedication to myself as a footnote on its title page and a generous mention in the acknowledgements, for which I remain most grateful and not a little proud. Since 2017 Peter has moved from being Director of the University of Cape Town’s FitzPatrick Institute of African Ornithology to being an Emeritus Professor in the Institute, so joining me in retirement. We first met and went on sea and shorebird surveys together when he was still a schoolboy, and I was in my 20s. In between then and now we have visited and worked together on most of the oceanic islands covered in his guide. Good memories!
Reference:
Ryan P.[G.] 2023. Guide to Seabirds of Southern Africa. Second Edition. Cape Town: Struik Nature. 200 pp. ISBN 978-1-77584-847-9. Paperback, many photographic illustrations. South African Rands 270.00. www.struiknature.co.za.
John Cooper, Emeritus Information Officer, Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels, 07 November 2023
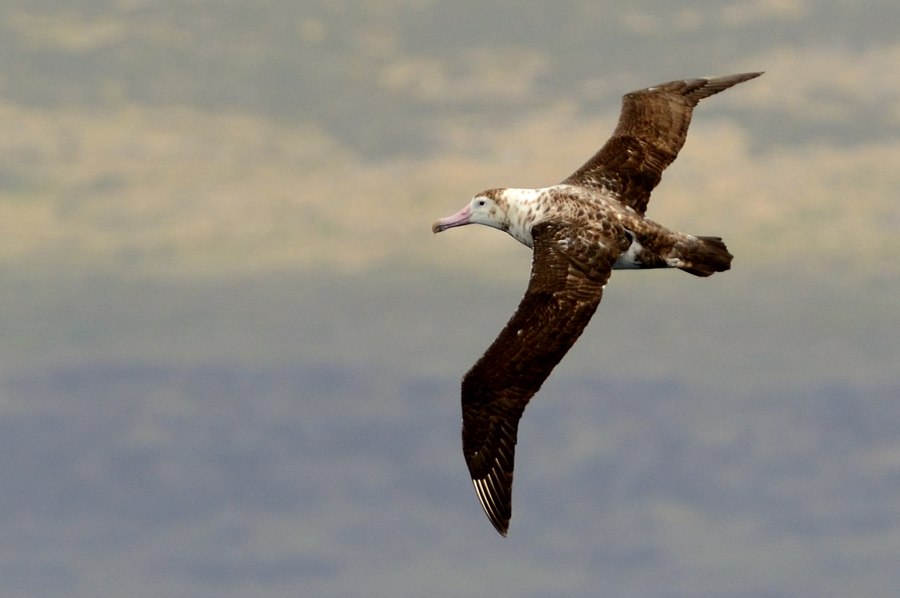 32 seabird species were identified as occurring in the Southern Indian Ocean Fisheries Agreement (SIOFA) management area, including the Endangered Amsterdam Albatross Diomedea amsterdamensis
32 seabird species were identified as occurring in the Southern Indian Ocean Fisheries Agreement (SIOFA) management area, including the Endangered Amsterdam Albatross Diomedea amsterdamensis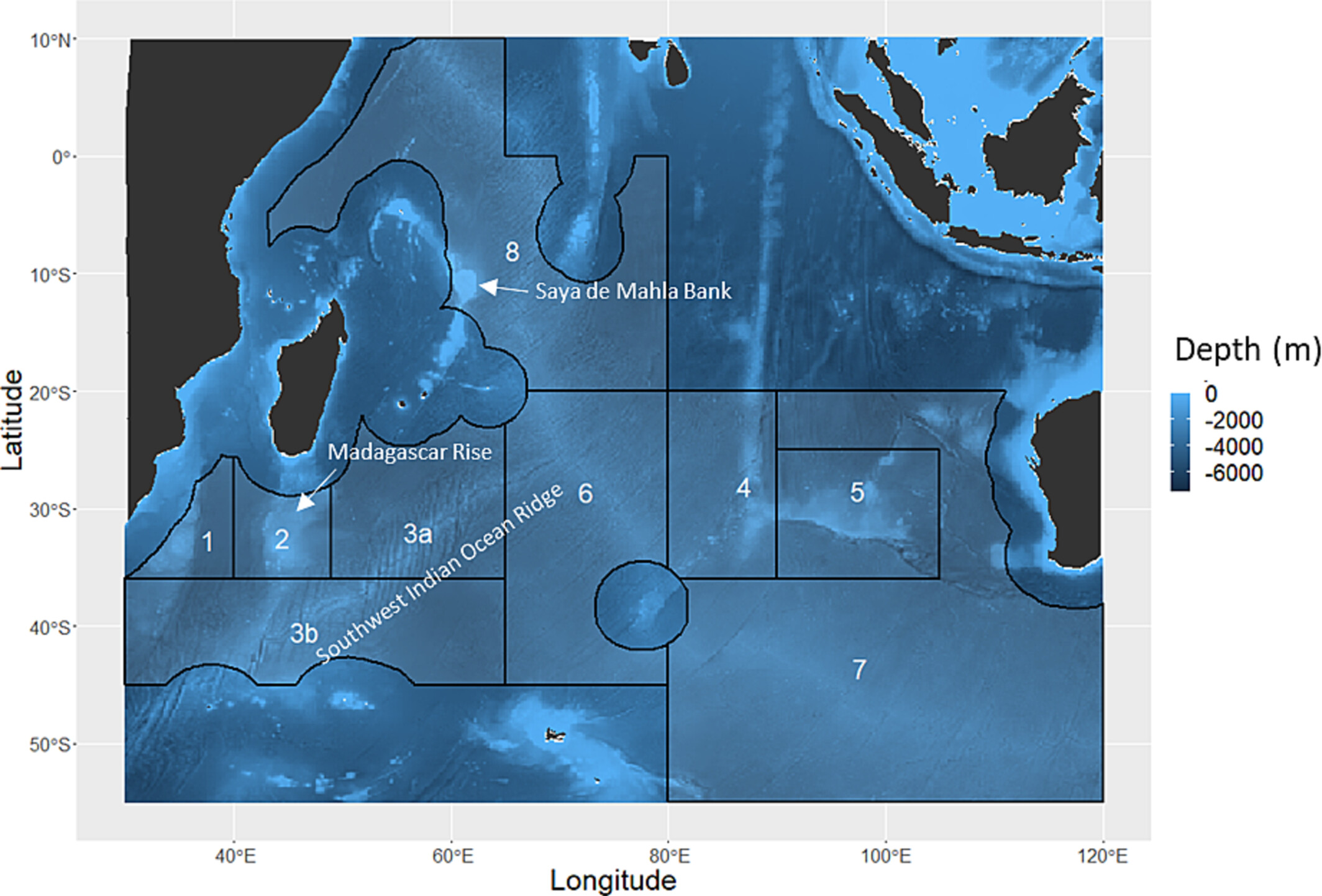

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 
 (Photos left - right) Agustina with Dr Ingrid van Putten from the CSIRO and with Dr Christine Bogle on her visit to the ACAP Secretariat in Hobart
(Photos left - right) Agustina with Dr Ingrid van Putten from the CSIRO and with Dr Christine Bogle on her visit to the ACAP Secretariat in Hobart Seeing the sights! Agustina enjoying a walk in Mount Field National Park, Tasmania (left), and taking in Wallaman Falls, in the Girringun National Park, Queensland (right).
Seeing the sights! Agustina enjoying a walk in Mount Field National Park, Tasmania (left), and taking in Wallaman Falls, in the Girringun National Park, Queensland (right).

 It's way back in 1984 and the ‘Fitztitute’ team is hamming it up for the camera on Gough Island. Peter is on the left, I am on the right, with Barry Watkins, Stevi Broni and the late Jim Enticott
It's way back in 1984 and the ‘Fitztitute’ team is hamming it up for the camera on Gough Island. Peter is on the left, I am on the right, with Barry Watkins, Stevi Broni and the late Jim Enticott