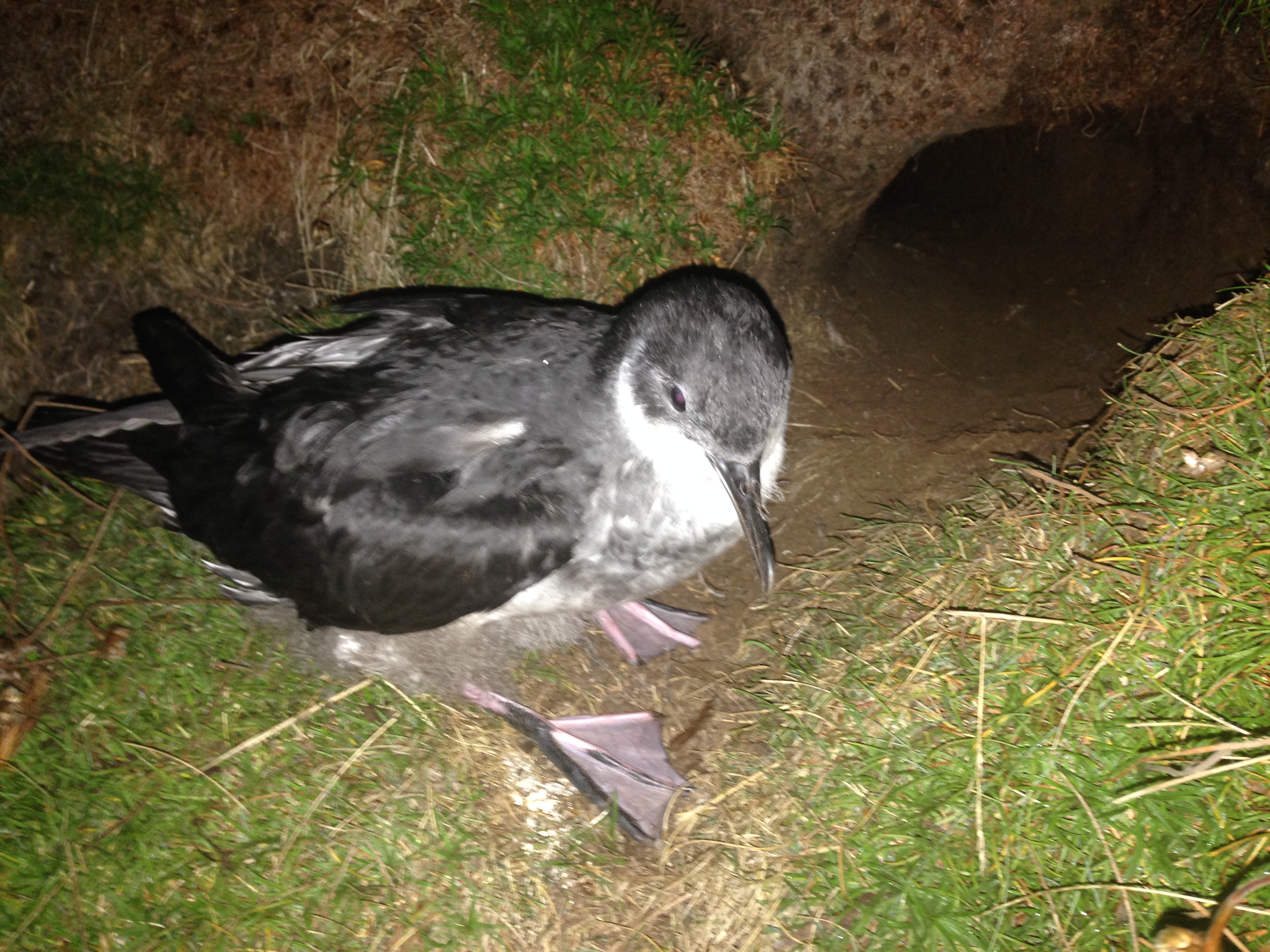
 A Manx Shearwater chick outside its burrow, photograph by Jaclyn Pearson
A Manx Shearwater chick outside its burrow, photograph by Jaclyn Pearson
Jason Matthiopoulos (School of Biodiversity, University of Glasgow, UK) and colleagues have published open access in the journal Endangered Species Research on the population dynamics of Manx Shearwaters Puffinus puffinus on the Scottish island of Rum in relation to planned offshore wind farm developments.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“The Isle of Rum (Scotland) holds ~30% of the world’s Manx shearwater population. The status and vulnerability of this internationally important and remote population are currently in question, mainly because of variations in field survey methodologies used on Rum across the years. This is particularly urgent in light of proposed offshore wind farm developments in the area. Here, we aimed to reconstruct population and demographic trends and quantify future sensitivities using a Bayesian state-space model. Fitting the model to simulated data of a similar nature and extent as the real data confirmed our ability to retrieve hidden parameters and reconstruct latent population trends in partially observed or wholly unobserved demographic time series. Applying these methods to the real data revealed that the population has been increasing since the 1980s but may now be starting to plateau. We extended the temporal horizon to a 100 yr forecast and ran several counterfactual scenarios relating to anthropogenic impacts on adult mortality and fecundity. These experiments indicated that the population is robust to strong pulse perturbations (e.g. wind farm construction or epidemic outbreaks), but vulnerable to small, sustained perturbations in adult survival (e.g. low-level mortality due to nearby wind farm operation). By integrating different data types collected by varying field methods over mismatched time windows, we have gained valuable insights into the status of this difficult-to-monitor species. Impact assessments for planned offshore wind developments around Rum should focus on collision and displacement costs to provisioning adults borne by wind farm operation (rather than construction).”
Reference:
Matthiopoulos, J., Thompson, K., Watt, L., O’Brien, S. & Furness, R.[W.] 2025. Reconstructing and forecasting the dynamics of an internationally important population of Manx shearwaters. Endangered Species Research 56: 291-303.
John Cooper, Emeritus Information Officer, Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels, 06 March 2026

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 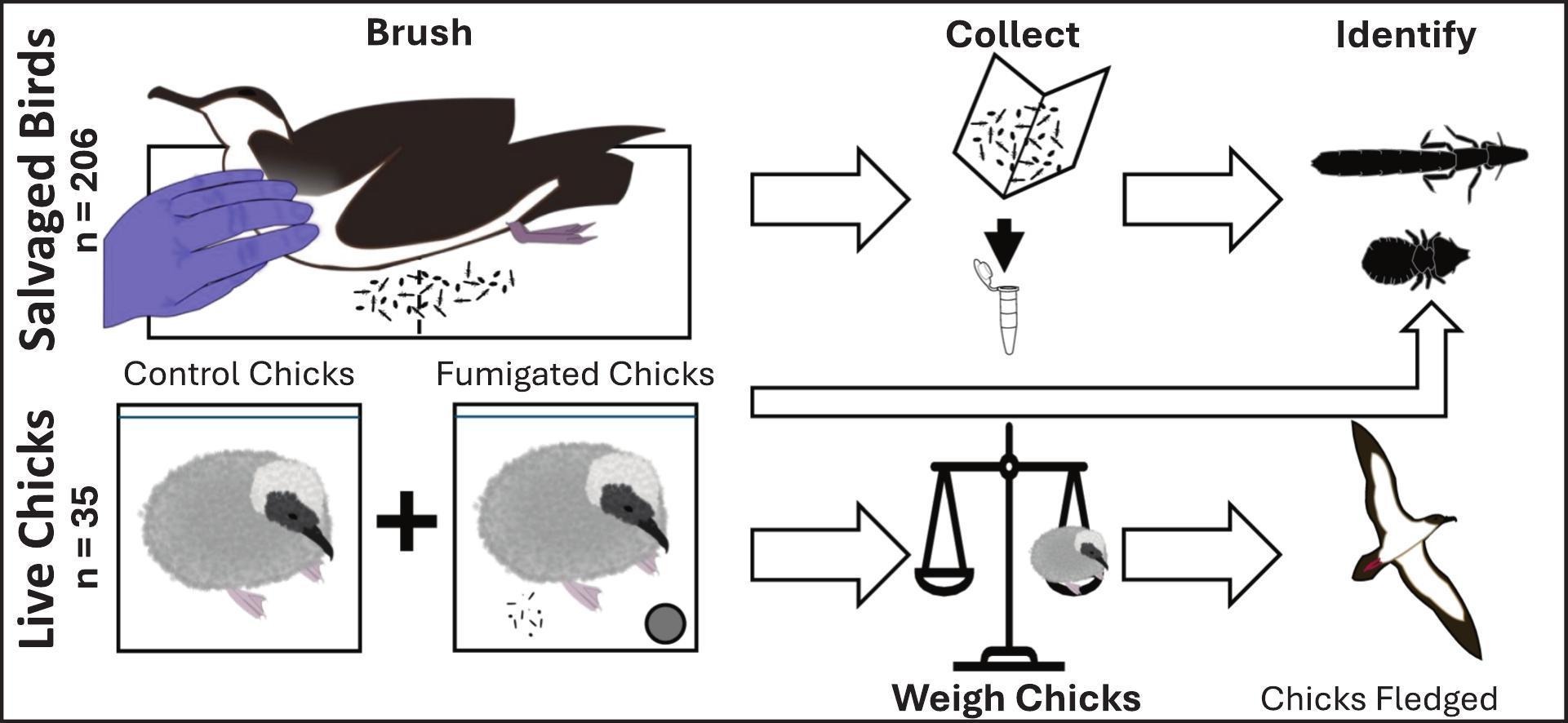 Graphical abstract from the publication
Graphical abstract from the publication






 ABUN artist, Deepti Jain is a Mumbai-based wildlife artist from India whose work focuses on portraying threatened species with sensitivity and depth. Working in charcoal, soft pastels, oils and watercolours, she seeks to capture both the physical presence and quiet dignity of her subjects, using art as a means to foster awareness of habitat loss and species vulnerability.
ABUN artist, Deepti Jain is a Mumbai-based wildlife artist from India whose work focuses on portraying threatened species with sensitivity and depth. Working in charcoal, soft pastels, oils and watercolours, she seeks to capture both the physical presence and quiet dignity of her subjects, using art as a means to foster awareness of habitat loss and species vulnerability.
