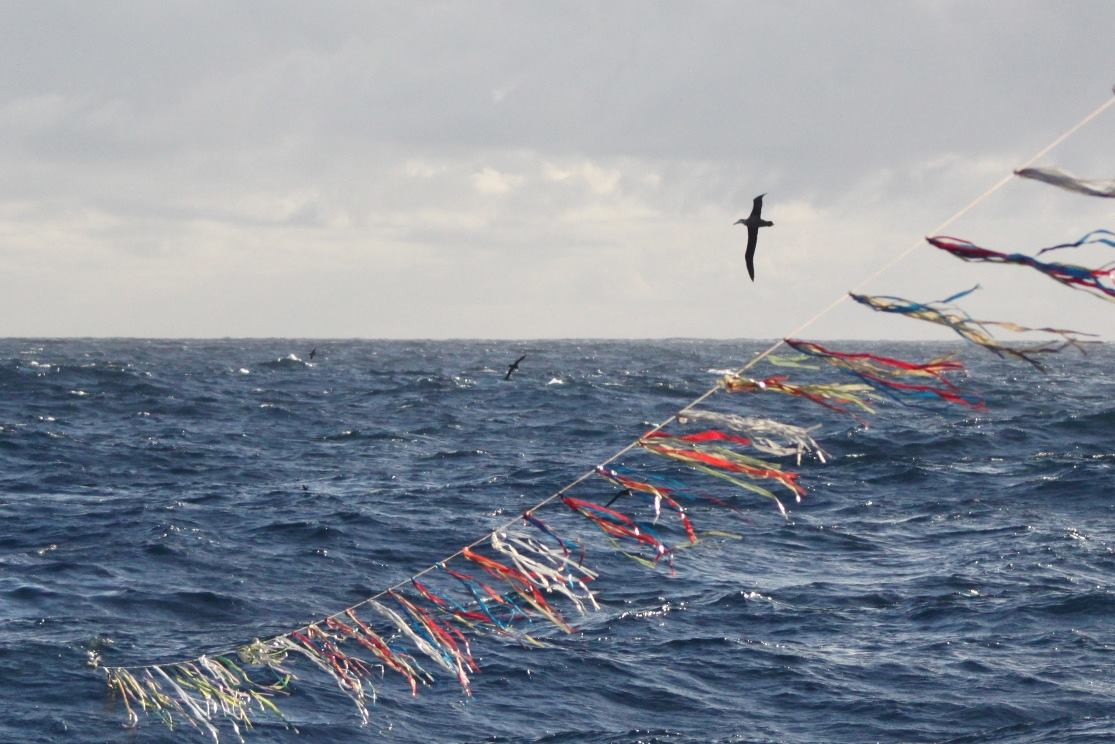
Best practice mitigation: a bird-scaring line with its coloured streamers flapping in the wind, photograph from Projeto Albatroz
The Seventh Session of the Meeting of the Parties (MoP7) to the Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP) held virtually over 9-13 May concluded with all Parties agreeing much work remains to be done in addressing threats to seabird populations. The meeting was chaired by Gaia Puleston of Australia.
Reflecting on the task ahead in her opening address to MoP7, Her Excellency the Honourable Barbara Baker AC, the Governor of the State of Tasmania, said: “The world is watching how you work together to conserve imperilled albatrosses and petrels. The future of these species depends on your collective efforts. I wish all participants at the Seventh Session of the Meeting of the Parties every success in ensuring there is a secure foundation upon which to advance the work of ACAP in the coming triennium.”
In 2019, ACAP's Advisory Committee declared a conservation crisis, which continues to be the most serious threat faced by its 31 listed species, with thousands of albatrosses, petrels and shearwaters dying every year as a result of fisheries operations.
The implementation of ACAP’s Best Practice seabird bycatch mitigation advice by ACAP Parties, non-Party Range States and, critically, Regional Fisheries Management Organisations (RFMOs) was identified as essential for the conservation of these majestic seabirds.
ACAP has developed a comprehensive range of Best Practice Advice guidelines and factsheets containing proven mitigation measures that can be implemented by coastal States and distant water fishing nations to reduce seabird bycatch. These are available in multiple languages and can be accessed through the ACAP website.
Encouragingly, a growing number of RFMOs and other bodies have adopted several ACAP best practice measures in their operations leading to the reduction of seabird bycatch from longline and trawl fishing. Progress was also noted in work addressing land-based threats to seabirds, in particular programmes directed at the eradication of invasive species.
Dr Michael Double, who currently chairs the ACAP Advisory Committee (and was the MoP7 Vice Chair) in his report to the Parties, highlighted the urgent need to engage with RFMOs and other organisations in adopting ACAP best practice for fisheries to prevent further declines in the populations of albatrosses and petrels. He stated “the Advisory Committee continues to recommend that Parties, Range States and RFMOs promote and implement best-practice seabird mitigation measures, improve the collection and reporting of seabird bycatch data, implement priority monitoring and tracking studies and continue schemes to eradicate invasive species at breeding sites.” Improving this critical information is vital for the development of targeted future priority conservation actions.
The impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on ACAP’s activities was noted, with progress of some ACAP activities slowed. With the easing of restrictions across the globe, it is hoped that ACAP can resume key activities, including restarting its grants and secondments programmes and continued engagement with RFMOs.
ACAP’s Executive Secretary, Dr Christine Bogle, commented that “this Meeting of the Parties reiterated the commitment of ACAP Parties and partner organisations to strive to protect these unique birds from the threats that they continue to confront.”
The report of the meeting will be available in ACAP's three official languages of English, French and Spanish in due course (click here), from where the MoP7 documents considered at the meeting may be viewed.
ACAP Secretariat, 24 May 2022


 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español