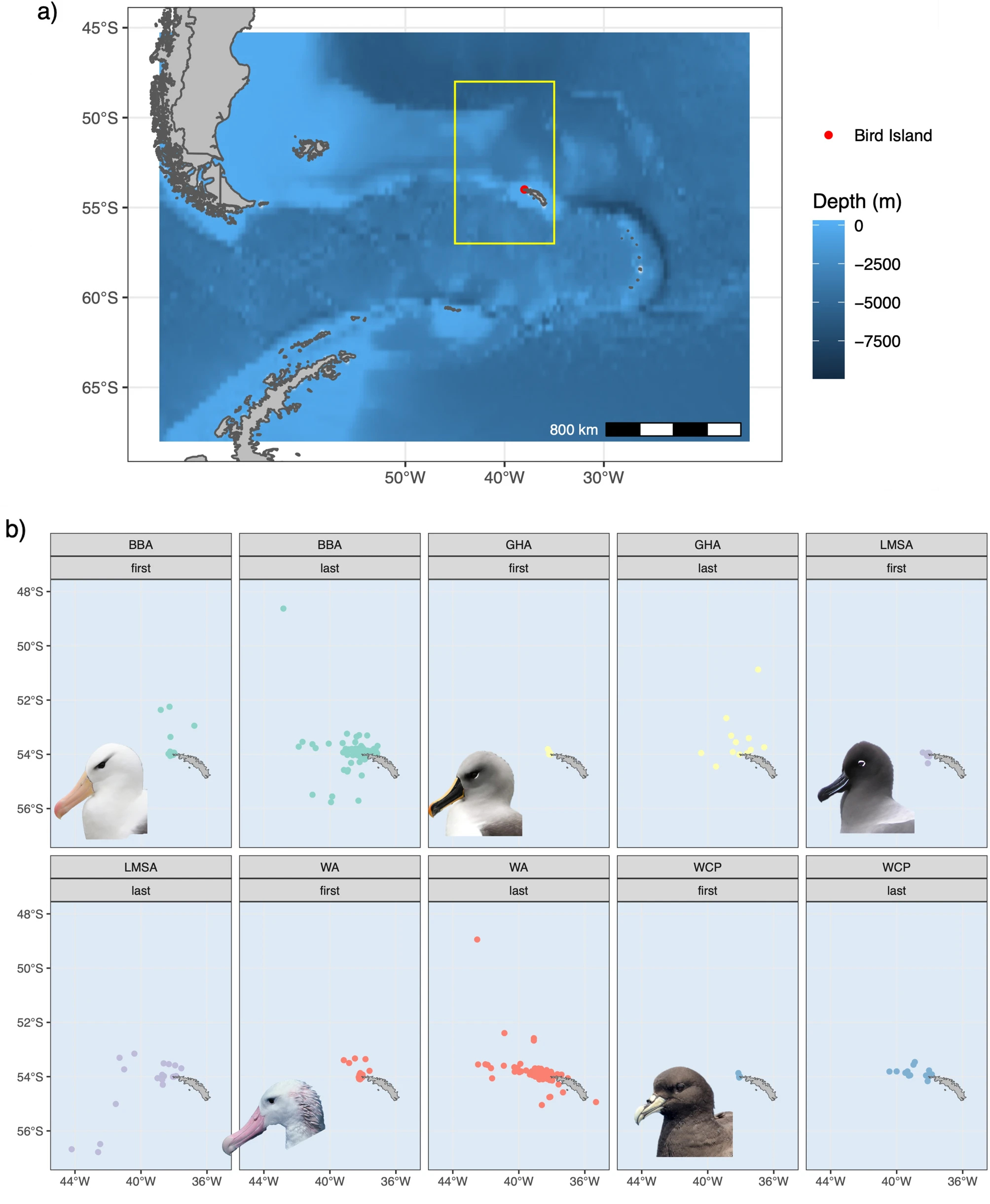
 Figure 1 as described in the paper: a Location of the study site: Bird Island, South Georgia. The yellow rectangle shows the location and extent of plots shown in the lower panes. b Location of first and last landings (wet bouts) during the foraging trips of seabirds tracked between 2008 and 2019 during the incubation (‘INC’), brood-guard (‘BR’) and post-guard (‘PB’) breeding stages. BBA black-browed albatross (Thalassarche melanophris), GHA grey-headed albatross (Thalassarche chrysostoma), LMA light-mantled albatross (Phoebetria palpebrata), WA wandering albatross (Diomedea exulans) and WCP white-chinned petrel (Procellaria aequinoctialis)
Figure 1 as described in the paper: a Location of the study site: Bird Island, South Georgia. The yellow rectangle shows the location and extent of plots shown in the lower panes. b Location of first and last landings (wet bouts) during the foraging trips of seabirds tracked between 2008 and 2019 during the incubation (‘INC’), brood-guard (‘BR’) and post-guard (‘PB’) breeding stages. BBA black-browed albatross (Thalassarche melanophris), GHA grey-headed albatross (Thalassarche chrysostoma), LMA light-mantled albatross (Phoebetria palpebrata), WA wandering albatross (Diomedea exulans) and WCP white-chinned petrel (Procellaria aequinoctialis)
Eleanor W. M. Kowalska O’Neil (Department of Environment and Geography, University of York, UK) and colleagues have published open access in the journal Polar Biology on the rafting behaviour of albatrosses and petrels in the South Atlantic.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Seabirds often spend time on the water in the vicinity of their breeding colonies at the start or end of foraging trips, which may be for bathing, social interaction, information transfer, or to reduce predation risk for small petrels that prefer to return to land in darkness. Although such behaviour (hereafter rafting) is common, there are few data on variation in its incidence or timing across species, or analyses of relationships with intrinsic or extrinsic factors such as breeding stage (reflecting central-place foraging constraints) or weather. Here, we use GPS and immersion data collected over multiple years at Bird Island, South Georgia, to investigate rafting behaviour of four albatross and one burrow-nesting petrel species. Nearly all tracked birds (89%) landed within 10 km of the colony at the start of foraging trips for ~ 30 min, whereas only 17% did so at the end, suggesting they likely use rafting mainly for plumage maintenance after extended breeding shifts on land. Rafting duration, distance and bearing from the colony varied markedly according to species, wind speeds and period of the day (daylight vs. darkness), which may reflect differences in foraging direction, time constraints, degree of plumage soiling, diel activity patterns, or the requirement for high wind speeds for efficient flight. Given that all the study populations are decreasing, and most individuals make extensive use of nearshore waters during the breeding season, effective marine spatial planning is required that eliminates or mitigates human risks around their colonies.”
Reference:
Kowalska O’Neil, E.W.M., Frankish, C.K. & Phillips, R.A. 2023. Rafting behaviour of albatrosses and petrels at South Georgia. Polar Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-023-03146-4
7 May 2023

 Français
Français  English
English  Español
Español